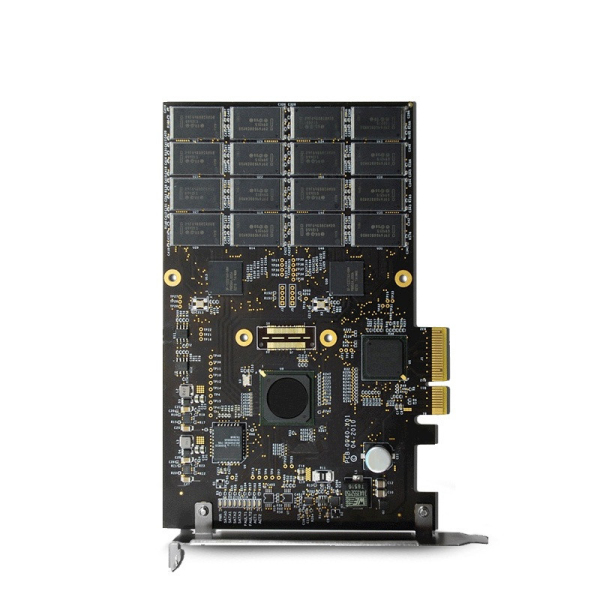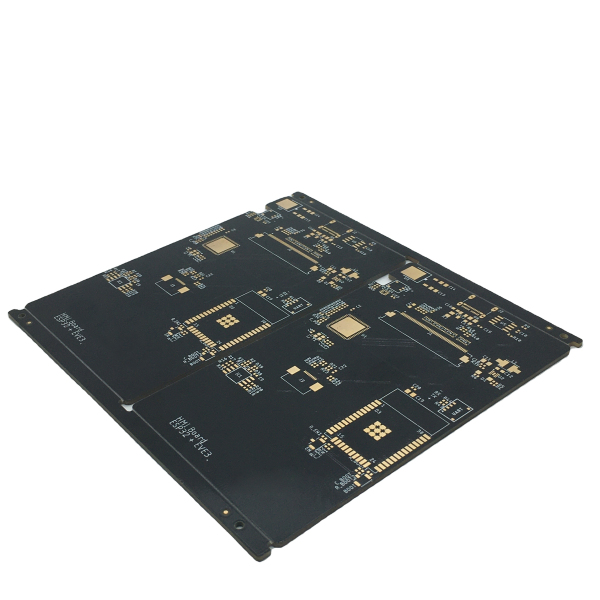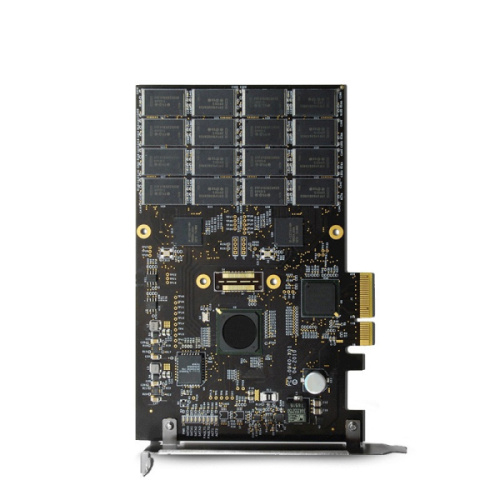
Flame Retardant Class 94V0 PCB
-
$0.06≥1 Piece/Pieces
- Min. Order:
- 1 Piece/Pieces
- Min. Order:
- 1 Piece/Pieces
Your message must be between 20 to 2000 characters
Contact Now
In PCB design, the same monitoring of PCB temperature requirements will cost more than balloons and ice cream. You need to know how much heat a PCB may withstand before it starts to suffer structural damage, especially if it is deployed in a high-temperature environment.
As you know, FR4 means Flame resistant PCB is the grade of F4 attribute. FR4 PCB is made of multilayer glass fiber epoxy laminate material. Because FR4 PCB has the same physical characteristics, it is the first choice in custom pcb fabrication.
FR4 PCB is very strong when exposed to high temperatures, but its physical properties will change at a certain temperature. The heat resistance of FR4 is represented by Tg or glass transition temperature, at which temperature it changes from a solid state to a soft and rubbery state. Generally, the rated Tg of FR4 PCB is 130°C.
In other words, if a PCB with a rated temperature of 130°C is heated above its glass transition temperature, it will lose its solid form. Not only your mechanical structure is unstable, but also the electrical performance of the PCB will decrease when the rated Tg is exceeded. This is why the importance of the maximum fr4 temperature must be considered when designing PCBs for applications such as oil and gas and automobiles where the temperature exceeds the typical Tg value.
If the application requires a PCB with a higher Tg value, you need to choose a PCB with a medium or high Tg. Medium Tg PCBs usually have a maximum temperature exceeding 150°C, while high Tg PCBs have a rated temperature exceeding 170°C. PCBs with higher Tg values also have better moisture resistance and chemical resistance, as well as a stronger physical structure under thermal conditions.
Unless otherwise specified, custom pcb fabrication will be manufactured using low Tg PCB. Medium and high Tg PCBs are usually more expensive. Materials such as S1141 and S1002-M are usually used to produce high Tg PCBs. Due to the higher glass transition temperature, the lamination of high Tg PCBs involves a lot of heat. In terms of price, high TG PCBs are more expensive.
Some applications require high Tg PCBs.
A common mistake is to use the tG value to determine the operating temperature of the PCB. When choosing the right FR4 PCB, a margin of at least 20°C should always be allocated. For example, the lower Tg FR4 is 130°C, which should have an operating temperature limit of 110°C.
As a PCB designer, you need to understand the thermal regulation technology in the design. The power regulation module will generate heat, and proper heat dissipation technology should be used. The use of heat sinks or heat dissipation vias can help prevent hot spots from overheating, which can cause the temperature of the PCB to exceed its limit.
The Tg rating and the operating temperature of the PCB are not the only factors that determine its function in high-temperature environments. The operating temperature limit of a single component must also be considered in the design.