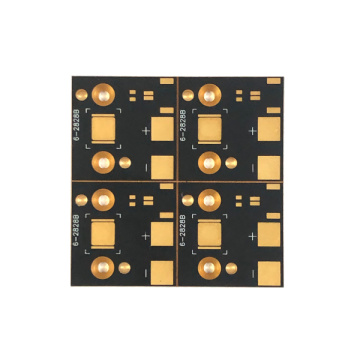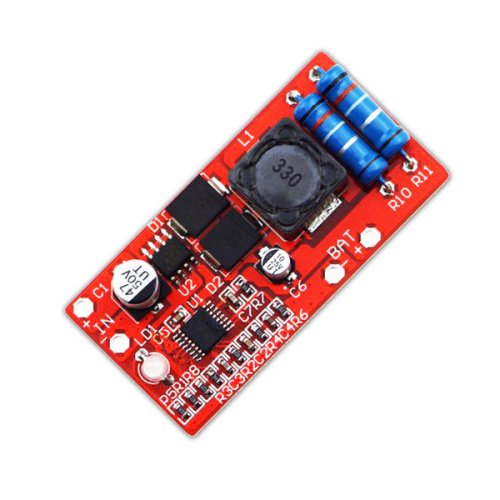
4 Layers 94v0 gamepad electronic pcb board
-
$1.87≥1 Piece/Pieces
- Min. Order:
- 1 Piece/Pieces
- Min. Order:
- 1 Piece/Pieces
Your message must be between 20 to 2000 characters
Contact NowWhat are the disadvantages of using FR4-based PCB?
The characteristics of FR-4 material make it versatile and affordable. This is why it is widely used in printed circuit manufacturing.
FR4 material and performance
FR4 is a standard for glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin compounds defined by NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association).
FR stands for "flame retardant" in English, and indicates that the material meets the UL94V-0 flammability standard for plastic materials. Code 94V-0 was found on all FR-4 PCBs. When the material catches fire, it ensures that the fire does not spread and goes out quickly.
For high TG or HiTG, the glass transition temperature (TG) is 115°C to 200°C, depending on the manufacturing method and the resin used. A standard FR-4 PCB will consist of a FR-4 layer sandwiched between two thin copper laminates.
FR-4 uses bromine. This chemical element is called halogen and has fire resistance. It replaces G-10, another compound with lower resistance in most applications.
The advantage of FR4 is that it has a good strength-to-weight ratio. It does not absorb water, maintains a high mechanical load and good insulation capacity in a dry or humid environment.
FR-4 example
Standard FR4: As the name suggests, it is standard FR-4, with a heat resistance of about 140°C to 150°C.
FR4 high TG: This type of FR-4 has a higher glass transition temperature (TG) at 180°C.
FR4 high CTI: Tracking index greater than 600 volts (or French IRC stands for driving resistance index).
FR4 without copper laminate: ideal for insulating boards, templates and clips
Thickness factors to consider
Component compatibility: Although FR-4 is used to manufacture many types of printed circuit boards, its thickness will affect the type of components used. For example, THT components are different from other components and require a thin PCB.
Space saving: Space saving is very important for the design of electronic cards, especially for USB connectors and Bluetooth accessories. Thinner cards are used in configurations where space economy is critical.
Design and flexibility: Most manufacturers prefer thick cards to thin cards. For FR-4, if the size of the card increases, there is a risk of cracking a substrate that is too thin. Thicker cards are very flexible and can be used to make "V-shaped grooves", also known as grooves.
The environment where the PCB is used should be considered. For electronic control units in the medical field, a thin PCB can reduce stress. Cards that are too thin (and therefore too flexible) are more sensitive to heat. They may bend and form undesirable angles during the part welding stage.
Impedance control: The thickness of the circuit board means the thickness of the dielectric, in this case FR-4, which makes impedance control easier. When impedance is an important factor, therefore the thickness of the card is a deterministic criterion that must be considered.
Connection: The type of connector used in the printed circuit also determines the thickness of FR-4.
Reasons for choosing FR4
Due to its low price, FR4 is the standard choice for small batch production of electronic boards or electronic prototypes.
However, FR4 is not ideal for high-frequency printed circuits. Similarly, if you want to integrate electronic boards into products that are not easy to use components and are not suitable for rigid printed circuit boards, you should choose another material-polyimide/polyamide.

Related Keywords