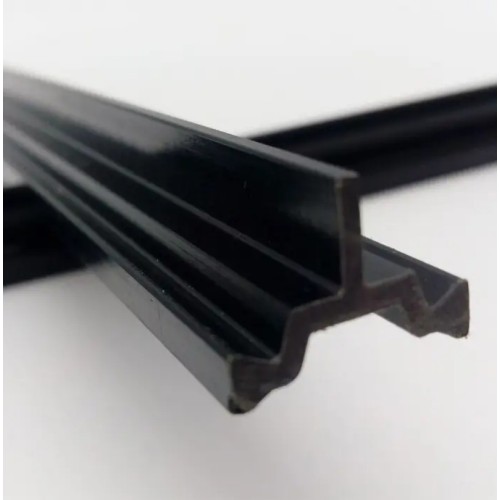
PA66 GF25 Polyamide Strip Stripe
- Min. Order:
- 1
- Min. Order:
- 1
- Transportation:
- Ocean, Land, Air, Express
- Port:
- Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Hongkong
Quantity:
Your message must be between 20 to 2000 characters
Contact NowBasic Info
Basic Info
| Supply Ability: | 1000 |
|---|---|
| Transportation: | Ocean,Land,Air,Express |
| Port: | Shenzhen,Guangzhou,Hongkong |
Product Description
Product Description
PA66GF25 is a high-performance, high-grade thermal insulation strip material. The following is a detailed analysis of its grade:
1. Material Composition and Characteristics
Material Composition: PA66GF25 is primarily composed of polyamide 66 (PA66) and 25% glass fiber. This composite material combines the excellent properties of PA66 with the reinforcing effects of glass fiber.
Properties: It features an extremely high melting point, excellent heat resistance, and self-extinguishing properties. It can maintain its shape at temperatures up to 240°C and has a tensile strength exceeding 80 MPa. Additionally, PA66GF25 demonstrates superior bonding strength, thermal insulation performance, aging resistance, high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, UV resistance, and weather resistance.
2. Application Areas and Advantages
Application Areas: PA66GF25 insulation strips are widely used in building applications such as thermal break aluminum windows and doors, serving as critical components for insulation and thermal performance.
Advantages: Compared to PVC thermal insulation strips, PA66GF25 offers higher strength and better durability. It is resistant to aging, deformation, or breakage, maintaining stable thermal insulation performance over extended periods. Additionally, PA66GF25 has excellent compatibility with aluminum alloy profiles, effectively blocking heat transfer and enhancing the thermal insulation performance of doors and windows.

Thermal Break Aluminum Window and Door Insulation Strip Material Selection: Differences Between PA66 and PVC and Identification Methods
When discussing “thermal break aluminum” and “thermal break aluminum-plastic composite windows,” we mentioned the importance of thermal insulation hard plastic materials, which act as a barrier to block heat transfer between the inner and outer frames of aluminum alloy. So, what are the considerations for this thermal insulation hard plastic material? Next, we will delve into the secrets of this critical component in “thermal break aluminum”—the thermal break strip.
1. The Importance of Thermal Break Strips
Thermal break strips play a crucial role in “thermal break aluminum,” and their application requires them to possess both “high strength” and “low thermal conductivity.” If the strength is insufficient, the thermal break aluminum profiles may fracture at the thermal break strip connection points, posing serious safety hazards to doors, windows, and curtain walls; conversely, if thermal conductivity is too high, it will impair thermal insulation performance. National standards specify stringent requirements for the thermal insulation profiles (i.e., thermal break strips) used in thermal break aluminum profiles.
First, let's understand the specific application of thermal break strips in thermal break aluminum profiles. Thermal break aluminum profiles using the strip insertion method typically employ polyamide profiles, while those using the casting method utilize polyurethane thermal insulation adhesive. In actual production, the strip insertion method is more widely adopted, with its key component, polyamide 66 (PA66), being a commonly used material in the industry. Currently, high-quality thermal break strips on the market mostly use PA66 GF25 thermal break strips. This material combines nylon 66 with 25% glass fiber, offering high bonding strength, excellent thermal insulation performance, as well as heat resistance, corrosion resistance, UV resistance, and good weather resistance. It also has a high compatibility with the profiles.
High-quality thermal break products typically clearly label the PA66 GF25 designation and also include the national recommended standard GB/T for compliance. Additionally, control requirements explicitly prohibit the use of materials such as PA6, PVC, and ABS. Given these explicit prohibitions, there may still be cases where these materials are used under certain circumstances.
2. Comparison of PA66 and PVC
Next, we will briefly compare the performance characteristics of these materials.
1. Tensile strength: The tensile strength of PA66 GF25 thermal insulation strips far exceeds that of PVC, reaching over 120 MPa, while PVC only achieves 50–80 MPa.
2. Heat deflection temperature: PA66 GF25 thermal insulation strips can withstand temperatures up to 240°C, far exceeding the 90°C limit of PVC thermal insulation strips.
3. Light and Heat Sensitivity: In both ambient and high-temperature environments, PVC thermal insulation strips tend to become brittle, leading to easy breakage; in contrast, PA66 nylon thermal insulation strips maintain their stability.
4. Aging resistance: PA66 GF25 thermal insulation strips are durable and resistant to aging; in contrast, PVC thermal insulation strips are prone to aging due to their light and heat sensitivity, potentially leading to situations where “the aluminum profiles have not yet aged, but the PVC thermal insulation strips need to be replaced first.”
5. Coefficient of thermal expansion: The coefficient of thermal expansion of PA66 GF25 thermal insulation strips is consistent with that of aluminum alloy, while PVC thermal insulation strips have a significantly different coefficient.
Due to the significant performance differences between these two materials, their prices also vary. Considering market price conditions, we can understand why there is such a significant price difference in thermal break aluminum window and door products, with part of the reason stemming from the materials used.
3. How to Distinguish Between PA66 and PVC
When discussing the performance and price differences of thermal break aluminum window and door products, we must focus on the comparison between their key raw materials, PA66 and PVC. To help you better discern the quality of thermal break aluminum products when purchasing, we will now delve into how to distinguish between these two materials.
1. Observe the glossiness. First, visually inspect the glossiness of the thermal break strip. If the thermal break strip has uniform color, no white spots, a matte texture, and a darker color, with synchronous gear imprints at both ends, it is likely made of nylon PA66. If the color is whitish, grayish-black, and the surface feels rough but abnormally shiny, be cautious as it may be low-quality PVC thermal break strip.
2. Conduct a burning test. If it is difficult to distinguish between the two thermal break strips based on appearance, you can try the burning method. The melting point of PA66 material can reach up to 220°C or even 310°C, while PVC only has a melting point of 80°C. Therefore, when ignited, nylon PA66 insulation strips burn slowly, continue burning or extinguish slowly after being removed from the flame, with the upper part of the flame appearing golden yellow and the lower part blue, and emitting a burnt feather or nail odor. In contrast, PVC insulation strips produce a larger flame when ignited, accompanied by a plastic odor.
3. Attempt to break them. Both types of insulation strips can be broken by hand, but the sound and fracture characteristics differ. PA66 nylon insulation strips produce a crisp sound when broken, with a clean, undistorted fracture surface that can be rejoined. PVC insulation strips, however, are soft and flexible, making them difficult to break; they often require multiple folds to break, and the fracture surface appears white and deformed.
Additionally, some professional users suggest using an oven test method: set the oven to 245 degrees and bake for fifteen minutes. If the thermal insulation strip does not soften, it is PA66; if it softens, it may be PA6 or an inferior counterfeit product; PVC will completely melt at 170 degrees.
In summary, understanding these methods aims to help consumers make basic judgments about materials when selecting aluminum alloy windows and doors, thereby choosing more reliable and suitable products.
Related Keywords
Related Keywords