
3G electrical wiring with Threaded PVC pipe building wire
Quantity:
Your message must be between 20 to 2000 characters
Contact NowBasic Info
Basic Info
| Place of Origin: | Guangdong, China (Mainland) |
|---|
Product Description
Product Description
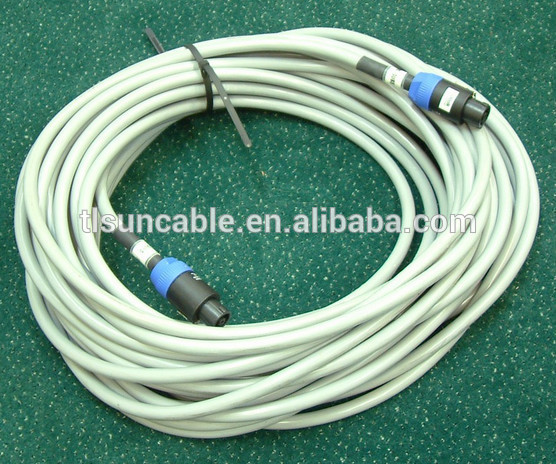
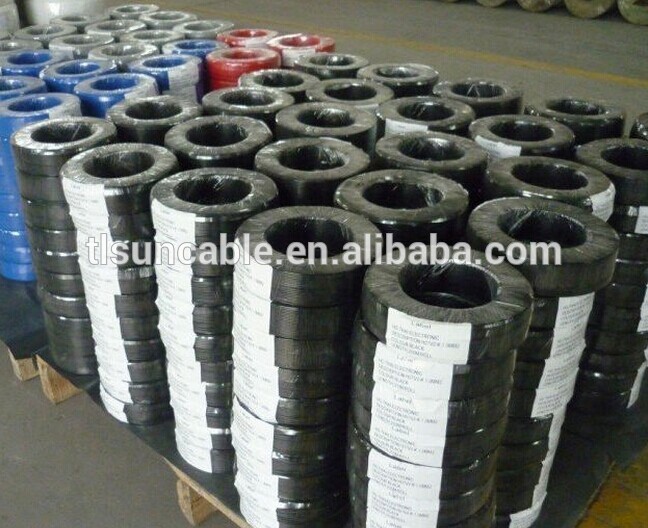
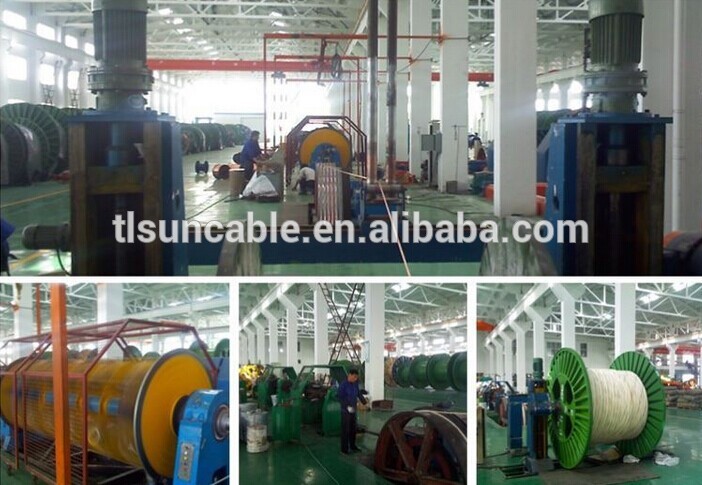
 3G electrical wiring with Threaded PVC pipe buliding wire Building wiring is the electrical wiring and associated devices such as switches, meters and light fittings used in buildings or other structures. Electrical wiring uses insulated conductors. Wiring safety codes vary by country, and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is attempting to standardise wiring amongst member countries. Wires and cables are rated by the circuit voltage, temperature and environmental conditions (moisture, sunlight, oil, chemicals) in which they can be used. Colour codes are used to distinguish line, neutral and ground (earth) wires. In Australia and New Zealand, the AS/NZS 3000 standard, commonly known as the "wiring rules", specifies requirements for the selection and installation of electrical equipment, and the design and testing of such installations. The standard is mandatory in both New Zealand and Australia; therefore, all electrical work covered by the standard must comply. In European countries, an attempt has been made to harmonise national wiring standards in an IEC standard, IEC 60364 Electrical Installations for Buildings. Hence national standards follow an identical system of sections and chapters. However, this standard is not written in such language that it can readily be adopted as a national wiring code. Neither is it designed for field use by electrical tradesmen and inspectors for testing compliance with national wiring standards. By contrast, national codes, such as the NEC or CSA C22.1, generally exemplify the common objectives of IEC 60364, but provide specific rules in a form that allows for guidance of those installing and inspecting electrical systems. The international standard wire sizes are given in the IEC 60228 standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission. In North America, the American Wire Gauge standard for wire sizes is used.
3G electrical wiring with Threaded PVC pipe buliding wire Building wiring is the electrical wiring and associated devices such as switches, meters and light fittings used in buildings or other structures. Electrical wiring uses insulated conductors. Wiring safety codes vary by country, and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is attempting to standardise wiring amongst member countries. Wires and cables are rated by the circuit voltage, temperature and environmental conditions (moisture, sunlight, oil, chemicals) in which they can be used. Colour codes are used to distinguish line, neutral and ground (earth) wires. In Australia and New Zealand, the AS/NZS 3000 standard, commonly known as the "wiring rules", specifies requirements for the selection and installation of electrical equipment, and the design and testing of such installations. The standard is mandatory in both New Zealand and Australia; therefore, all electrical work covered by the standard must comply. In European countries, an attempt has been made to harmonise national wiring standards in an IEC standard, IEC 60364 Electrical Installations for Buildings. Hence national standards follow an identical system of sections and chapters. However, this standard is not written in such language that it can readily be adopted as a national wiring code. Neither is it designed for field use by electrical tradesmen and inspectors for testing compliance with national wiring standards. By contrast, national codes, such as the NEC or CSA C22.1, generally exemplify the common objectives of IEC 60364, but provide specific rules in a form that allows for guidance of those installing and inspecting electrical systems. The international standard wire sizes are given in the IEC 60228 standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission. In North America, the American Wire Gauge standard for wire sizes is used. 





Related Keywords
Related Keywords










